Global Translational Research
Vascular and orthopedic complications of sickle cell disease
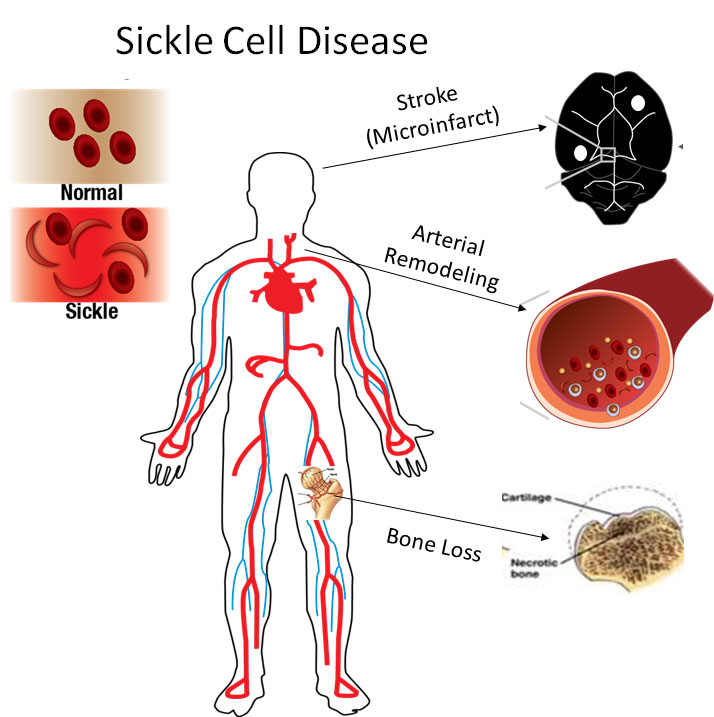
Children with sickle cell disease have an 11% chance of suffering a major stroke by the age of 16, but 33% are at risk of having a silent stroke that impairs mental function and cognitive abilities. We are investigating the cellular and inflammatory mechanisms accelerating these destructive tissue remodeling.
Computational fluid dynamics of blood flow in the cerebrovasculature
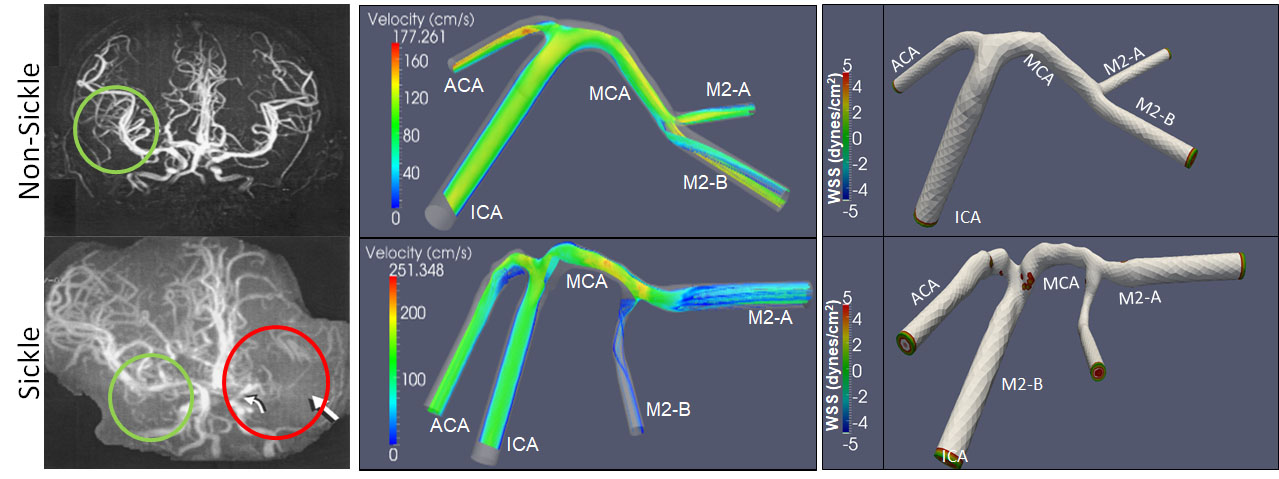
Hemodynamic parameters of the blood in sickle cell disease change its properties and can influence cell and tissue mechanic properties in the vasculature. Computational fluid dynamics models of disturbed blood flow in these individuals are currently being developed using human data as well as transgenic mouse models in our research laboratory and with our collaborators in Beijing as part of BME PKU program.
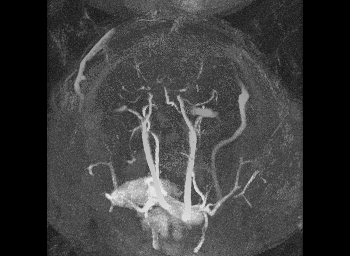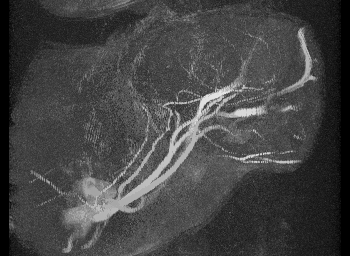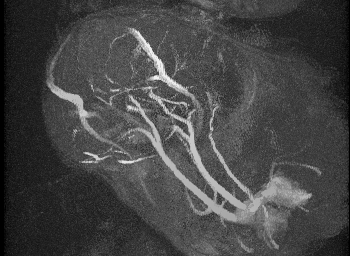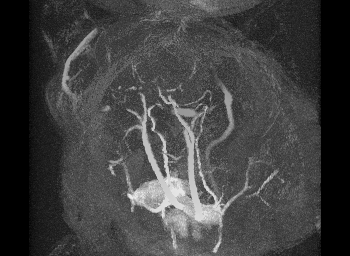
Sickle Cell Large Artery Biomechanics and Imaging
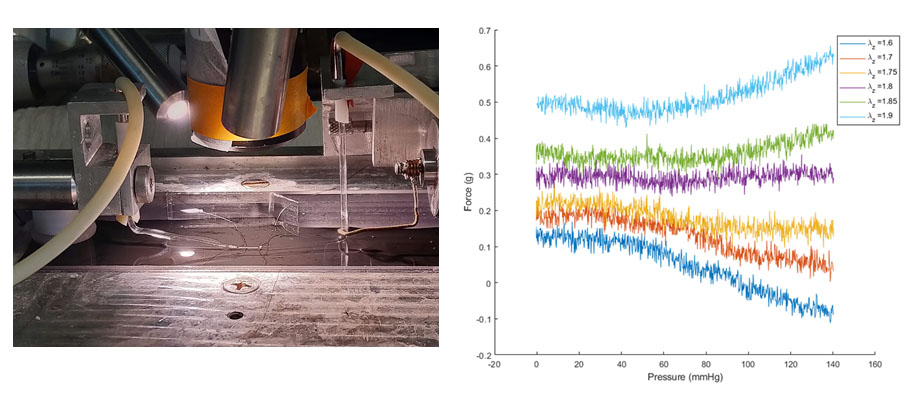
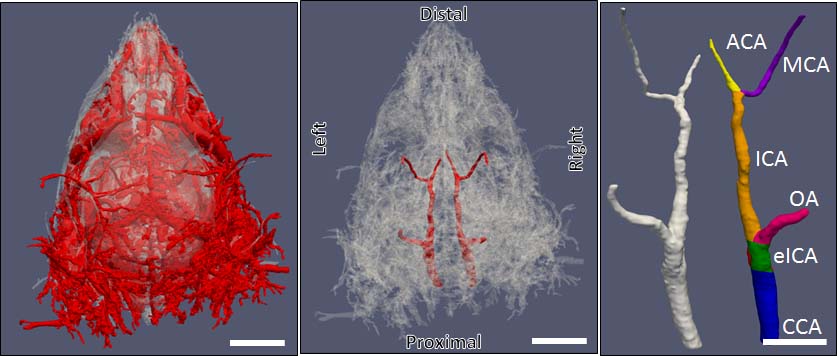
Mechanical testing of carotid arteries and aortas from mice with sickle cell disease allows us to understand the changes to the elastin and collagen structures as they are remodeled due to upregulation of cathepsins in response to sickle cell disease. Cerebral arteries are more difficult to visualize so we use a label free method of magnetic resonance angiography.
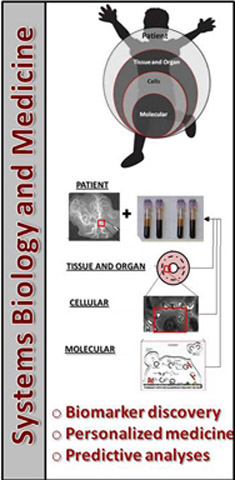
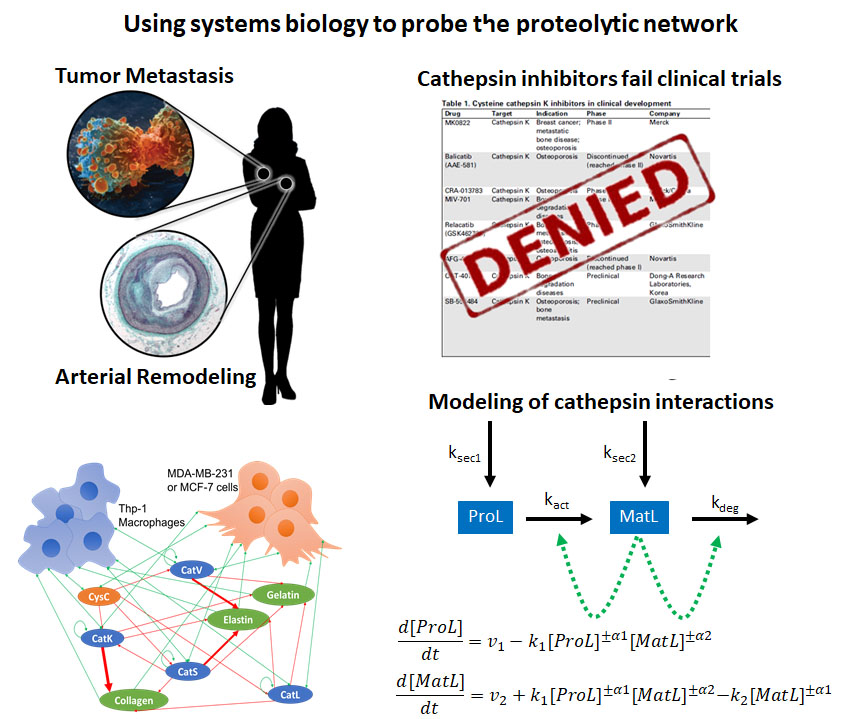
Systems Biology and Personalized Medicine
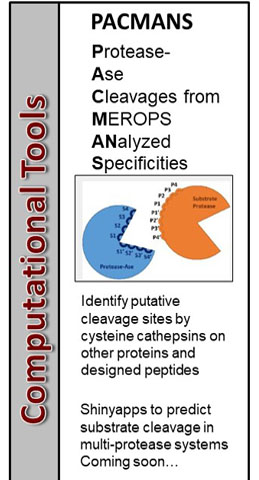
Cathepsin Proteolytic Network Analyses
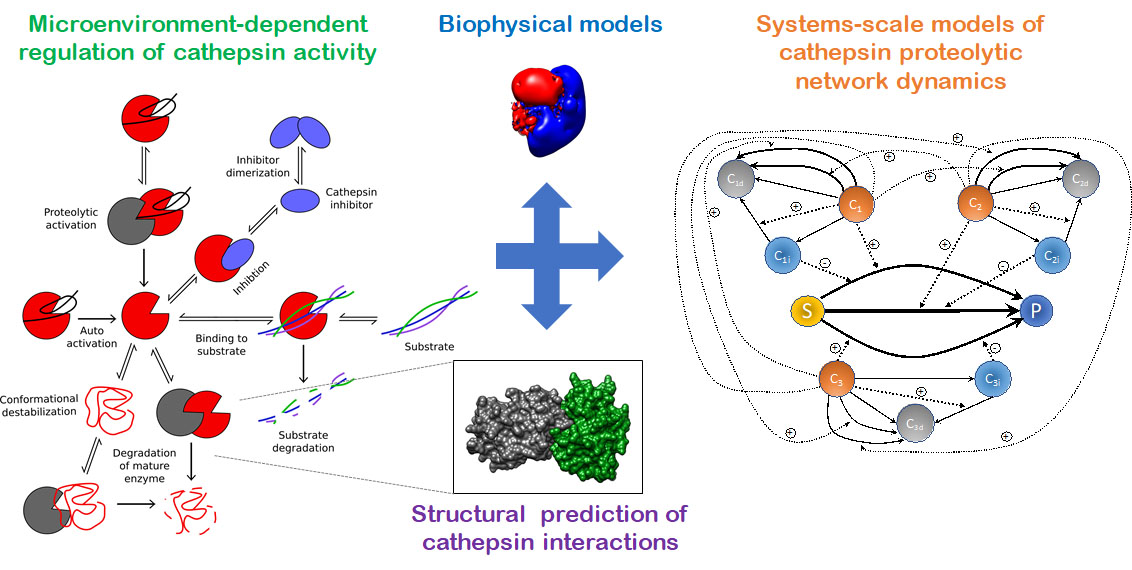
Personalized Proteolytic Potential to Predict Disease Progression and Response to Therapy
Aggressive Breast Cancer in Young Women in Ethiopia
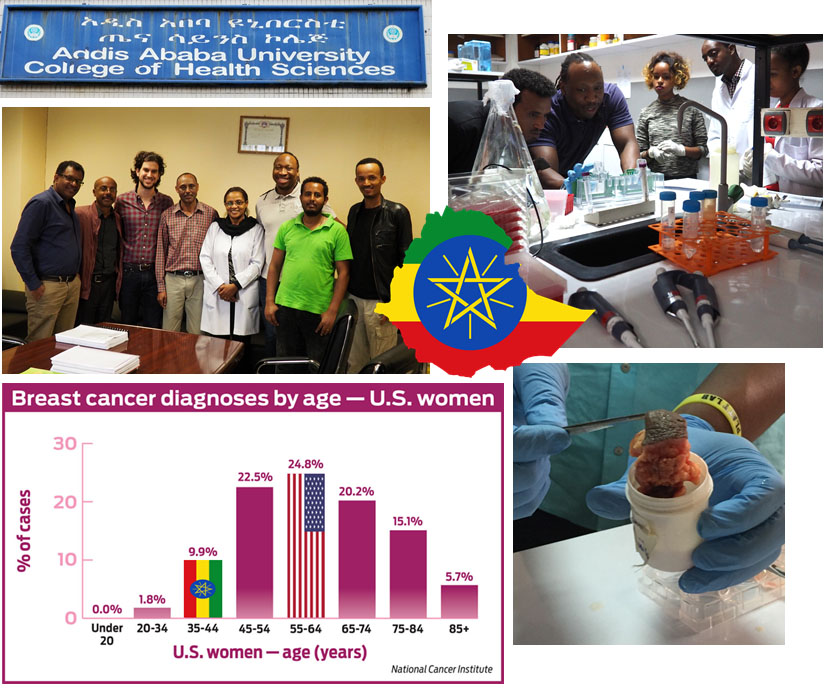
Women in Ethiopia develop extremely aggressive breast cancer, and this can occur at very young ages such as their 20s or 30s. Our hypothesis is that tumors in Ethiopian women are more proteolytically active leading to aggressive growth and invasion. Proteolytic profiling would determine why some women present with more advanced tumors at earlier ages, but low cost methods are needed for practical translation to this beautiful country.
Emergent Behaviors of Integrated Cellular Systems
Fibrin(ogen)olytic Properties of Cysteine Cathepsins: Relevance for Biobots and in Sickle Cell Disease
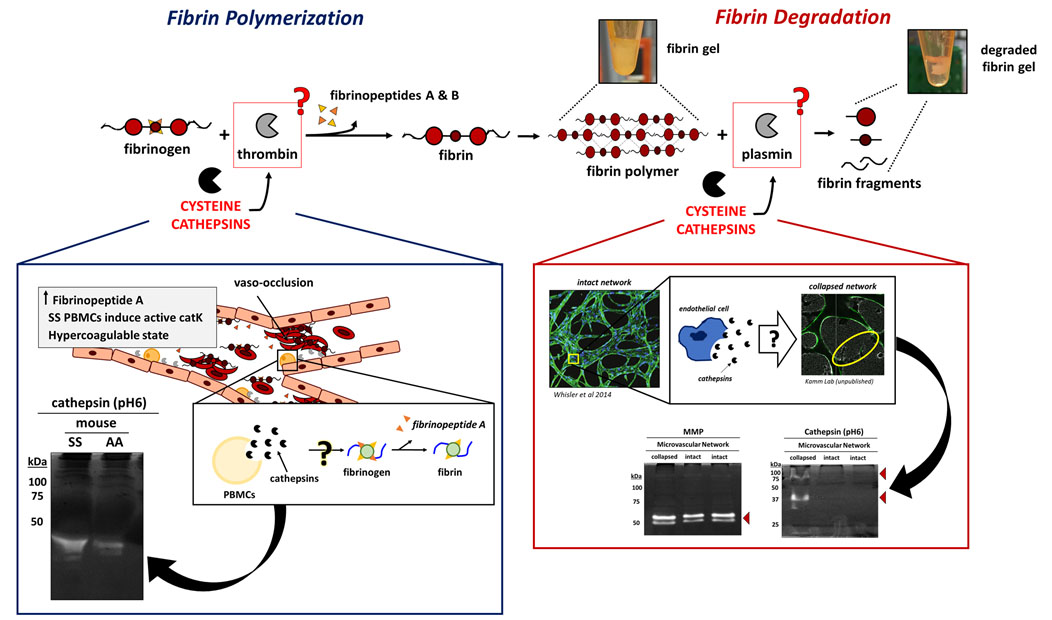
Potential roles in destabilizing fibrin-based engineered living systems, and in abnormal blood clotting mechanisms in sickle cell disease.